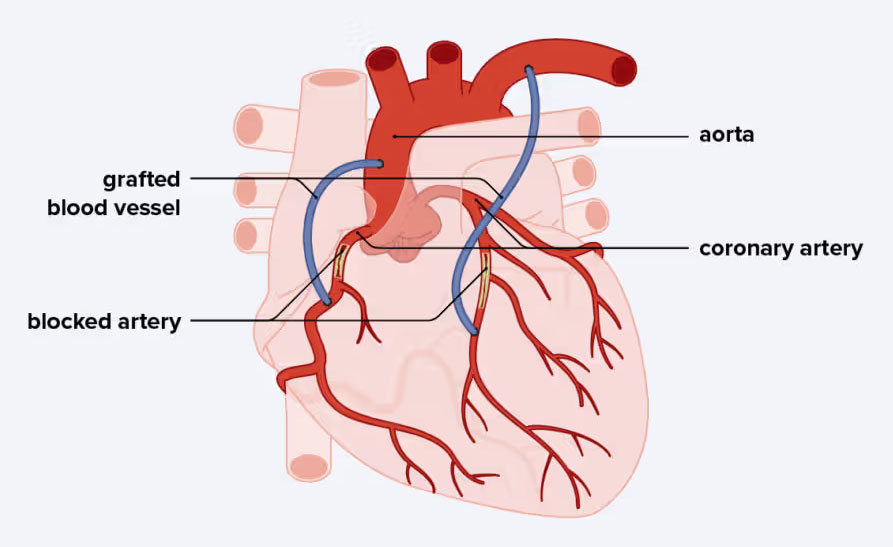
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a surgical procedure used to treat severe coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which the blood vessels supplying the heart become narrowed or blocked. During the procedure, a healthy blood vessel—typically taken from the leg, arm, or chest—is grafted to bypass the blocked portion of the coronary artery. This allows oxygen-rich blood to flow more freely to the heart muscle, reducing chest pain (angina) and improving heart function. CABG is often recommended when lifestyle changes, medications, or less invasive interventions like angioplasty are not sufficient.
Modern CABG surgery may involve on-pump (using a heart-lung machine) or off-pump (beating heart) techniques, depending on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s approach. The procedure has proven benefits in improving quality of life, increasing life expectancy in certain high-risk groups, and reducing the risk of heart attacks. Recovery typically involves a hospital stay of about a week, followed by cardiac rehabilitation to support long-term heart health and physical recovery.