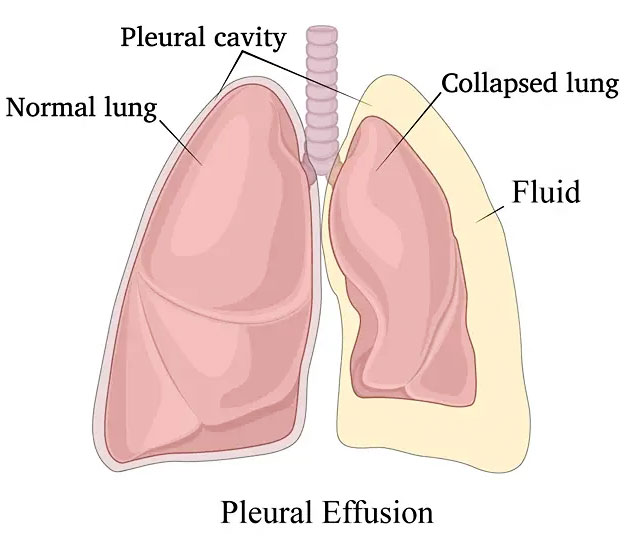
Surgical treatment for pleural diseases addresses conditions affecting the pleura, the thin membrane surrounding the lungs. Common pleural conditions requiring surgery include empyema (infection with pus accumulation in the pleural space) and pneumothorax (collapsed lung due to air in the pleural space). Empyema often follows pneumonia or chest infections and may need surgical drainage if antibiotics and chest tubes are insufficient. Pneumothorax, particularly recurrent or large ones, may require intervention to remove air and prevent recurrence. Prompt surgical management helps restore lung expansion and prevent long-term damage.
Surgical options include video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and open thoracotomy, depending on the severity and complexity of the disease. In empyema, procedures such as decortication (removal of thickened pleura and pus) can help re-expand the lung. For pneumothorax, pleurodesis (fusion of pleural layers) or bleb resection (removal of air-leaking areas) is commonly performed. Minimally invasive techniques like VATS offer excellent visualization, reduced pain, and faster recovery. These surgeries are essential to improve breathing, prevent recurrence, and ensure complete recovery in patients with pleural disease.